
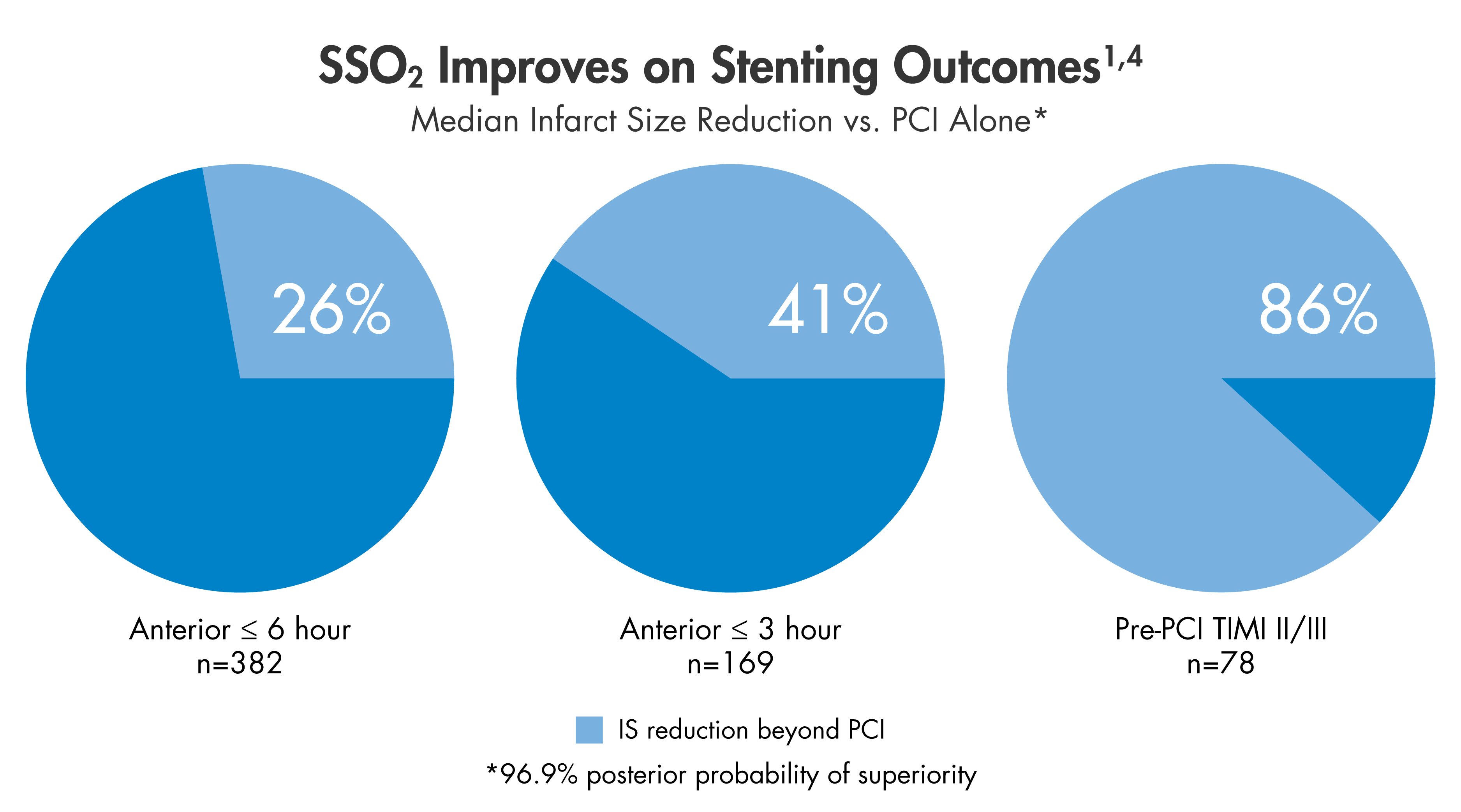
TherOx has conducted several clinical studies to establish the safety and effectiveness of SSO2 Therapy. In total, nearly 800 patients have been clinically evaluated. The pivotal randomized AMIHOT II clinical trial met its pre-specified endpoints, demonstrating a 26% relative median size reduction and a non-inferior 30-day Major Adverse Cardiac Events (MACE) profile as compared to control subjects receiving the standard of care.1,2,3
Post hoc interpretation of subset data reveals an even more dramatic infarct size reduction benefit in patients with shorter times to reperfusion and better TIMI flow grade upon presentation.4 Infarct size reduction has been strongly associated with reductions in heart failure and death.5
Most recently, TherOx completed the IC-HOT confirmatory study, which included 100 patients at 15 U.S. centers. This study met its endpoint and demonstrated results consistent with AMIHOT I and AMIHOT II studies, confirming safety with the latest generation SSO2 Therapy system.6
Download a copy of the SSO2 Therapy Clinical Compendium.
1 Stone, et al. Circ Cardiovasc Interv. 2009 Oct; 2:366-375.
2 Posterior probability of superiority for smaller infarct size = 96.9%.
3 Posterior probability of non-inferiority in 30-day MACE (within a 6% safety margin) = 99.5%.
4 AMIHOT II subset data on file at TherOx, Inc.
5 Stone, et al. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2016;67(14):1674–83.
6 David SW, et al. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2018;1–9.
Caution: Federal (United States) law restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a physician. The TherOx DownStream System is indicated for the preparation and delivery of SuperSaturated Oxygen Therapy (SSO2 Therapy) to targeted ischemic regions perfused by the patient’s left anterior descending coronary artery immediately following revascularization by means of percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) with stenting that has been completed within 6 hours after the onset of anterior acute myocardial infarction (AMI) symptoms caused by a left anterior descending artery infarct lesion.